Overview of Copper Strip
Copper strips are versatile components used extensively in electrical, construction, and manufacturing industries due to their excellent conductivity, malleability, and resistance to corrosion. Here are some key parameters that define the characteristics and quality of copper strips:
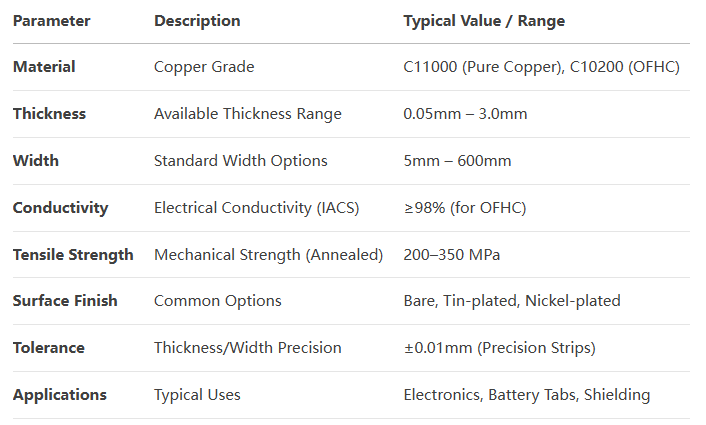
- Material Composition: Copper strips are primarily made of pure copper (Cu) with varying purity levels, commonly 99.9% for electrical applications. Common grades include C11000 (Electrolytic-Tough-Pitch, ETP) and C10100 (Oxygen-Free High Conductivity, OFHC).
- Dimensions: Copper strips are characterized by their thickness, width, and length. Thickness can range from fractions of a millimeter up to several millimeters, while widths and lengths are customized based on application requirements. Standard widths might range from 5mm to 600mm, and lengths can be supplied in coils or cut-to-size.
- Surface Finish: Strips can have various surface finishes, including bright annealed (BA), matte, or tinned. Bright annealed provides a smooth, reflective finish, while tinning adds a thin layer of tin for improved solderability and corrosion resistance.
- Temper: Copper strips can be supplied in different tempers, such as soft, half-hard, or hard, depending on the desired level of formability or stiffness required for the application.
- Electrical Conductivity: A crucial parameter for copper strips used in electrical applications, conductivity typically ranges from 58 to 60 MS/m for ETP copper and can exceed 100 MS/m for OFHC copper.
- Tensile Strength: This measures the strip’s resistance to breaking under tension. For ETP copper, it ranges from about 200 to 280 MPa, while OFHC copper may have a slightly lower tensile strength due to its higher purity.
- Elongation: Elongation percentage indicates the strip’s ductility, or how far it can stretch before breaking. Copper strips typically exhibit high elongation values, around 30% to 50%.
- Hardness: Measured using the Rockwell scale, hardness helps determine the strip’s resistance to indentation. Soft copper strips have a lower hardness value, suitable for forming, while harder tempers are more rigid.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper inherently resists corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor and marine applications. Tinned copper further enhances this property.
- Inspection and Testing: Copper strips are tested for dimensional accuracy, surface defects, conductivity, and mechanical properties to ensure they meet industry standards such as ASTM B152, ASTM B370, or international equivalents.
- Packaging: Copper strips are often coiled for ease of handling and transportation, with protective wrapping to prevent damage during transit.

copper strip
Characteristics and advantages of copper strips
High electrical and thermal conductivity: Copper strips have excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, suitable for electronic and heat dissipation applications.
Good flexibility and ductility: easy to bend, stamp and form, suitable for precision processing.
Corrosion resistance: strong oxidation resistance, suitable for humid or corrosive environments (such as tinned copper strips).
High-precision dimensional control: can produce ultra-thin (0.05mm) to thick (3mm) specifications to meet different needs.
Weldability and plating: easy to solder, silver solder or surface plating (such as nickel plating, gold plating).
Specifications of copper strips
Application of copper strips
Electronic industry: PCB circuit boards, flexible circuits (FPC), lead frames, shielding layers.
Power industry: transformer windings, cable shielding, conductive connectors.
New energy: lithium battery tabs, photovoltaic welding strips, electric vehicle battery connectors.
Industrial manufacturing: heat sinks, electromagnetic shielding, precision instrument components.
Decoration and packaging: metal inlays, crafts, anti-counterfeiting labels.
Company Profile
Copper-group is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12-year-experience in providing super high-quality copper and relatives products.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality copper products, please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.
Payment Methods of Copper strip
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Shipment of Copper strip
It could be shipped by sea, by air, or by reveal ASAP as soon as repayment receipt.
5 FAQs about copper strip
What are the common materials of copper tape?
Pure copper (T2), oxygen-free copper (TU1/TU2), phosphorus deoxidized copper (TP1/TP2), tinned copper tape, etc.
How thin can copper tape be?
Ultra-thin copper tape can reach 0.05mm and is often used in flexible circuits and precision electronics.
How to prevent copper tape from oxidation?
The surface is tinned, nickel-plated or coated with antioxidants, and kept dry during storage.
What is the difference between copper tape and copper foil?
Copper tape is thicker (usually >0.1mm) and has higher mechanical strength; copper foil is thinner (<0.1mm) and is used for copper clad laminates, etc.
Can copper tape be used for high-frequency signal transmission?
Yes, high-purity oxygen-free copper (OFHC) is suitable for high-frequency, low-loss scenarios.











