Overview of Copper Wire
Copper wires are essential components in electrical systems, known for their high conductivity, ductility, and reliability. Key parameters that define the characteristics and applications of copper wires include:
- Diameter (Gauge): Wires are commonly measured by their diameter, often expressed in American Wire Gauge (AWG) for electrical wiring in North America. Smaller AWG numbers indicate thicker wires. For example, 12 AWG is thicker than 24 AWG.
- Conductivity: This measures how well the wire conducts electricity and is usually expressed as a percentage of IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), where pure copper has a conductivity of about 100% IACS.
- Stranding: Wires can be solid or stranded (composed of multiple thinner wires twisted together). Stranded wire is more flexible and easier to work with, especially in applications requiring frequent bending.
- Insulation: The type of insulation coating the wire determines its suitability for different environments. Common insulations include PVC, XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), and Teflon, each designed for specific temperature ranges, chemical resistance, and mechanical protection.
- Temperature Rating: This indicates the maximum operating temperature the wire can withstand without damage to its insulation or degradation of its conductive properties.
- Voltage Rating: Specifies the maximum voltage the wire can safely carry without risk of electrical breakdown.
- Tensile Strength: Measures the wire’s resistance to breaking under tension, important for installation and long-term durability.
- Resistance: The opposition to electric current flow through the wire, typically measured in ohms per unit length and influenced by wire diameter, material, and temperature.
- Flexibility: Determines how easily the wire can bend without damage, crucial for installations in tight spaces or dynamic applications.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Copper itself is inherently corrosion-resistant, but surface treatments or coatings may enhance this property further for specific environments.

copper wire
Characteristics and advantages of copper wire
High conductivity: The conductivity of copper is second only to silver, making it an ideal material for power transmission and electronic components.
Excellent ductility: It can be drawn into extremely fine wires (micrometer level), suitable for precision electronics.
Strong corrosion resistance: Good oxidation resistance, suitable for humid or high temperature environments.
Good weldability: Easy to solder and silver solder, with high connection reliability.
Economical and efficient: Compared with materials such as silver and gold, it has lower cost and high cost performance.
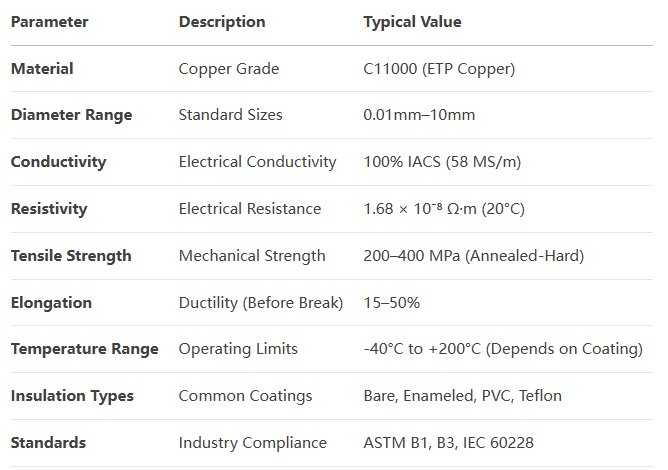
Specifications of copper wire
Application of copper wire
Power transmission: wires, cables, transformer windings.
Electronic industry: PCB circuits, coils, relays, connecting wires.
Communication equipment: optical fiber cable shielding layer, data line conductor.
Automotive industry: automotive wiring harnesses, sensor wires.
Household appliances: motor windings, heating elements, internal wiring.
Company Profile
Copper-group is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12-year-experience in providing super high-quality copper and relatives products.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality copper products, please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.
Payment Methods
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Shipment
It could be shipped by sea, by air, or by reveal ASAP as soon as repayment receipt.
5 FAQs of copper wire
Why is copper wire more commonly used than aluminum wire?
Copper has better conductivity, higher mechanical strength, and stronger oxidation resistance.
What is the role of tinning on the surface of copper wire?
Improve oxidation resistance, enhance welding performance, and prevent the formation of verdigris.
How to distinguish pure copper wire from copper-clad aluminum wire?
Measure resistance (copper wire has lower resistance) or cut and observe the cross section (copper-clad aluminum has an aluminum core).
Will copper wire fail at high temperatures?
Long-term temperatures exceeding 150°C may accelerate oxidation, so it is recommended to use high-temperature resistant enameled wire.
Can copper wire be used for high-frequency signal transmission?
Yes, but the skin effect is obvious at high frequencies, and silver-plated copper wire works better.











