Overview of copper pipe
Copper pipes are widely used in plumbing and HVAC systems due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to handle both hot and cold water. Key parameters that define the characteristics and uses of copper pipes include:
- Type: Copper pipes are classified into several types based on their wall thickness and intended use. The main types are Type K, Type L, and Type M, with Type K being the thickest and most robust, followed by Type L, and Type M being the thinnest.
- Diameter: Copper pipes are sized according to their outside diameter (OD), commonly ranging from 1/8 inch to 4 inches, with standard increments in between. The sizing can follow imperial (inches) or metric (millimeters) measurements.
- Wall Thickness: This impacts the pipe’s pressure rating and overall strength. Thicker walls (as in Type K) can handle higher pressures and are more resistant to external damage.
- Working Pressure: Refers to the maximum pressure the pipe can safely withstand during operation, varying depending on the pipe type, diameter, and temperature of the fluid it carries.
- Temperature Rating: Specifies the range of temperatures the pipe can effectively handle without damage or loss of performance. Copper is suitable for both hot and cold water applications.
- Coating/Finish: Copper pipes may have a plain finish or come with a coating such as lacquer to prevent tarnishing during storage and handling. For installations, special coatings may be applied to protect against corrosion.
- Jointing Method: Copper pipes are typically joined using soldering, brazing, or press-fit connections. Each method has its advantages, with soldering being traditional but requiring skill, while press-fit systems offer faster, no-solder installation.
- Hardness: Soft copper is more pliable and easier to bend, often used for refrigeration lines and in tight spaces where flexibility is crucial. Hard copper, on the other hand, is stiffer and better suited for straight runs and areas where rigidity is important.
- Refrigeration Grade: Certain copper pipes are specifically designed for refrigeration and air conditioning systems, with additional requirements for leak tightness and compatibility with refrigerants.
-
Longevity: Copper piping is known for its long service life, often exceeding 50 years, due to its inherent resistance to corrosion and degradation.

copper pipe
Characteristics and advantages of copper pipes
Excellent thermal conductivity: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity and is suitable for efficient heat exchange systems.
Strong corrosion resistance: Water-resistant and oxidation-resistant, suitable for humid environments such as water supply and refrigeration.
Antibacterial properties: Natural antibacterial properties, suitable for drinking water pipes and medical equipment.
Flexible and easy to process: can be bent, welded, brazed, and installed flexibly.
Long life & recyclable: long service life (more than 50 years), 100% recyclable, environmentally friendly and economical.
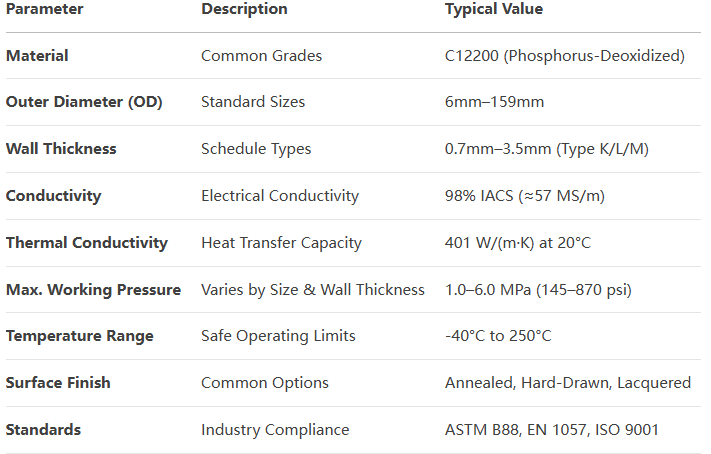
Specifications of copper pipes
Application of copper pipes
Building water supply and drainage: hot and cold water pipes, drinking water systems.
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC): refrigerant pipes, condensers, evaporators.
Industrial equipment: heat exchangers, hydraulic systems, compressed air pipes.
Medical & Food Industry: medical gas pipes, food processing equipment.
Energy & Power: solar water heaters, transformer cooling pipes.
Company Profile
Copper-group is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12-year-experience in providing super high-quality copper and relatives products.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality copper products, please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.
Payment Methods
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Shipment
It could be shipped by sea, by air, or by reveal ASAP as soon as repayment receipt.
5 FAQs about copper pipes
Will copper pipes rust?
Copper pipes are not easy to rust, but long-term exposure to acidic or high-sulfur environments may form patina (basic copper carbonate).
What are the advantages of copper pipes compared to PVC pipes?
Copper pipes are more durable, heat-resistant, UV-resistant, and do not release harmful substances.
Are copper pipes suitable for gas transmission?
Yes, but they must meet specific standards (such as ASTM B88) and ensure leak-free welding.
How to connect copper pipes?
Commonly used methods are brazing, press-fit, crimping, or threading.
Why are copper pipes more expensive than PPR pipes?
Copper pipes have high material costs, but they have a longer lifespan, low maintenance costs, and are more economical in the long run.











